Health Desk
Sandeep Dhand Nutritionist And Health Educator
Introduction
Osteogenesis Imperfecta, often called OI, is a rare genetic disorder that mainly affects the bones. People with this condition have very fragile bones, which means their bones can break easily, sometimes even without a clear injury. Because of this, Osteogenesis Imperfecta is also known as Brittle Bone Disorder.
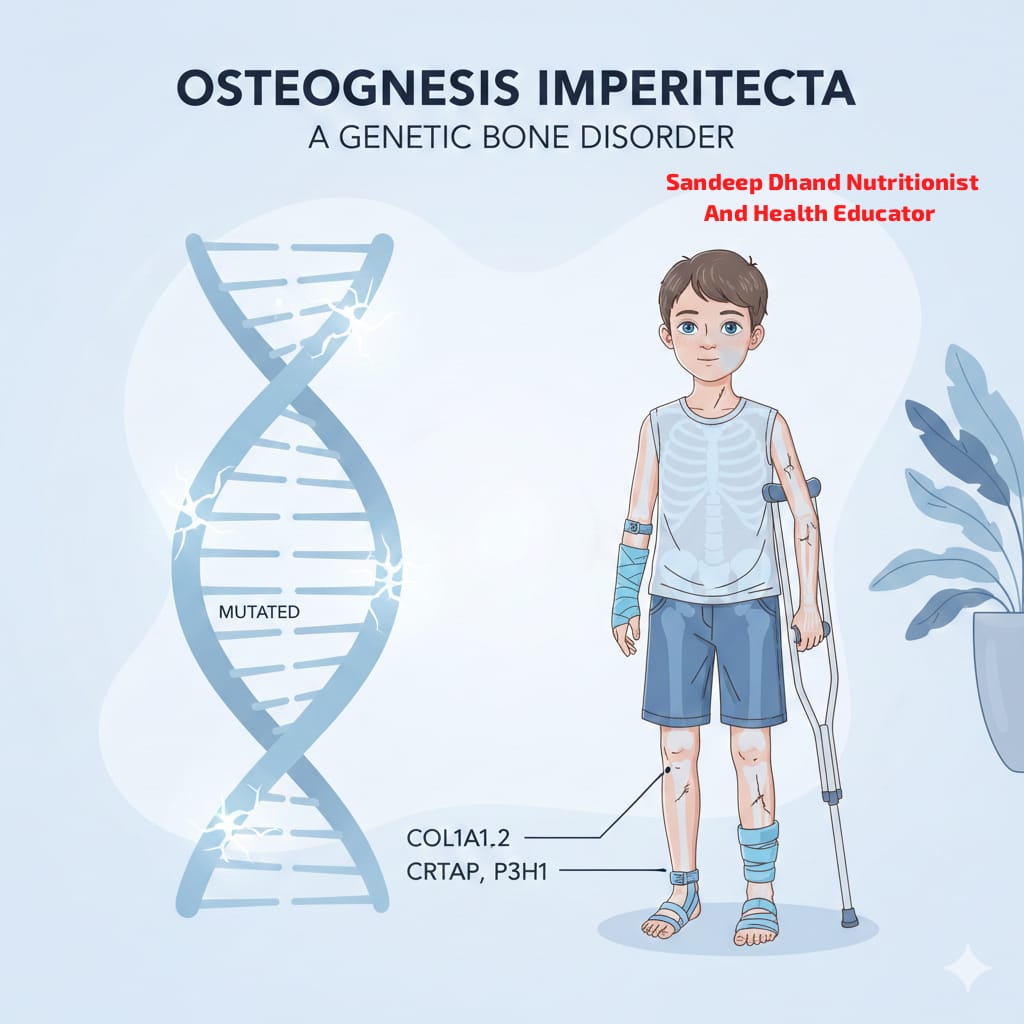
This condition is usually present from birth, but its severity can vary from person to person. Some people may have only a few fractures in their lifetime, while others may experience many fractures even during infancy or childhood. Apart from bones, Osteogenesis Imperfecta can also affect teeth, hearing, muscles, joints, and growth.
This article explains Osteogenesis Imperfecta in simple and easy English, covering its causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, daily care, nutrition, and life with the disorder.
What Is Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
Osteogenesis Imperfecta is a genetic disorder that affects how the body makes collagen. Collagen is a very important protein that gives strength and structure to bones, skin, muscles, and connective tissues.
In people with OI:
The body produces too little collagen, or
The collagen produced is not strong enough
Because of this defect, bones become weak, brittle, and easy to break.
Why Is It Called Brittle Bone Disease?
The word “brittle” means something that breaks easily. In Osteogenesis Imperfecta, bones lack strength due to poor collagen quality, so they can fracture with:
Minor falls
Simple movements
Coughing or sneezing (in severe cases)
That is why the condition is commonly known as Brittle Bone Disease.
Is Osteogenesis Imperfecta a Disease or a Disorder?
Osteogenesis Imperfecta is a disorder, not an infection or contagious disease.
It does not spread from person to person
It is not caused by food habits or lifestyle
It is usually inherited genetically
Causes of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Genetic Cause
The main cause of Osteogenesis Imperfecta is a mutation in genes responsible for making collagen. These genes are usually:
COL1A1
COL1A2
These genes control the production of Type 1 Collagen, which is essential for strong bones.
Inherited or New Mutation
OI can occur in two ways:
Inherited from parents
New genetic mutation (even if parents are healthy)
Types of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
There are several types of Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Some are mild, and some are severe.
Type 1 (Mild Type)
Most common form
Few fractures
Normal or near-normal height
Blue or gray tint in eyes
Normal lifespan
Type 2 (Most Severe)
Very severe form
Fractures present before birth
Underdeveloped lungs
Often life-threatening
Type 3 (Severe)
Many fractures from birth
Short stature
Bone deformities
Muscle weakness
Life expectancy varies
Type 4 (Moderate)
Moderate bone fragility
Some bone deformities
Normal eye color
Variable severity
Other rare types also exist, but these four are the most commonly described.
Symptoms of Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Symptoms depend on the type and severity, but common signs include:
Bone-Related Symptoms
Frequent bone fractures
Bone deformities
Curved spine (scoliosis or kyphosis)
Short height
Eye Symptoms
Blue, gray, or light-colored sclera (white part of the eye)
Dental Problems
Weak or discolored teeth
Easily broken teeth (dentinogenesis imperfecta)
Hearing Problems
Hearing loss, usually in teenage years or adulthood
Muscle and Joint Issues
Loose joints
Muscle weakness
Joint pain
How Is Osteogenesis Imperfecta Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on:
Medical history
Physical examination
X-rays showing multiple fractures
Bone density tests
Genetic testing (if available)
In some cases, OI is detected before birth through ultrasound.
Is There a Cure for Osteogenesis Imperfecta?
There is no permanent cure for Osteogenesis Imperfecta.
However, the condition can be managed effectively with proper medical care, therapy, and lifestyle support.
Treatment Options for Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Medical Treatment
Bisphosphonate drugs to strengthen bones
Pain management medications
Vitamin D and calcium supplements (under medical advice)
Surgical Treatment
Rods inserted into long bones to prevent fractures
Corrective surgeries for deformities
Physiotherapy
Strengthens muscles
Improves balance
Reduces fracture risk
Role of Nutrition in Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Good nutrition plays a very important role in managing OI.
Important Nutrients
Calcium
Vitamin D
Protein
Magnesium
Phosphorus
Foods That Help
Milk and dairy products
Leafy green vegetables
Nuts and seeds
Eggs
Fish
Fortified cereals
Foods to Avoid (in excess)
Very high salt foods
Excess caffeine
Junk food
Daily Life with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Living with OI requires:
Careful movement
Avoiding high-risk activities
Using assistive devices if needed
Regular medical follow-ups
Children with OI should be encouraged to:
Attend school
Socialize
Build confidence
Psychological and Emotional Support
People with Osteogenesis Imperfecta may face:
Fear of fractures
Anxiety
Low self-confidence
Support from:
Family
Counselors
Support groups
is very important for mental well-being.
Osteogenesis Imperfecta in Children
Children with OI need:
Early diagnosis
Safe handling techniques
Proper nutrition
Physiotherapy from an early age
With proper care, many children with OI grow up to live productive and meaningful lives.
Can People with OI Live a Normal Life?
Yes, many people with mild or moderate OI live:
Normal lifespans
Independent lives
Successful careers
The key is early management, awareness, and support.
Myths and Facts About Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Myth: OI is caused by poor diet
Fact: It is a genetic disorder
Myth: People with OI cannot work
Fact: Many live active professional lives
Myth: OI is contagious
Fact: It is not contagious at all
Importance of Awareness
Because Osteogenesis Imperfecta is rare:
Many people misunderstand it
Early diagnosis is often delayed
Spreading awareness helps:
Reduce stigma
Improve care
Support affected families
Conclusion
Osteogenesis Imperfecta is a genetic bone disorder that causes fragile bones due to defective collagen. While there is no cure, modern medicine, proper nutrition, physiotherapy, and emotional support can greatly improve quality of life.
With awareness, early treatment, and a supportive environment, people with Osteogenesis Imperfecta can live confident, meaningful, and fulfilling lives.