Sandeep Dhand
Nutritionist And Health Educator
Quinoa (pronounced “keen-wah”) has gained massive popularity in recent years as a “superfood.” It is often praised for its high nutritional value and versatility in the kitchen. But is quinoa truly good for health, or is it just a marketing trend? This article will dive deep into quinoa, its nutritional profile, benefits, and possible drawbacks, providing you with a comprehensive guide.
What is Quinoa?

Quinoa is a seed derived from the plant Chenopodium quinoa, native to South America, particularly the Andes region. Often mistaken for a grain, quinoa is technically a pseudocereal, meaning it is cooked and eaten like grains but does not belong to the grass family.
There are several types of quinoa, with the most common being:
- White Quinoa (mildest flavor).
- Red Quinoa (firmer texture).
- Black Quinoa (earthy taste).
Nutritional Value of Quinoa

One of quinoa’s greatest strengths lies in its impressive nutrient profile. Here’s a breakdown of its nutrients per 100 grams (cooked):
Calories: 120 kcal
Protein: 4.1 g
Carbohydrates: 21.3 g
Fiber: 2.8 g
Fats: 1.9 g (mainly unsaturated fats)
Vitamins: Rich in B vitamins (B1, B2, B6, and folate) and vitamin E.
Minerals: High in magnesium, phosphorus, iron, zinc, and potassium.
Antioxidants: Contains flavonoids like quercetin and kaempferol, known for their anti-inflammatory properties.
Unique Feature: Complete Protein
Unlike most plant-based foods, quinoa is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. This makes it especially valuable for vegetarians and vegans looking for alternative protein sources.
Why is Quinoa Considered Healthy?

- High in Protein for Muscle Health
Quinoa provides all essential amino acids, making it a high-quality protein source. This is crucial for muscle repair, growth, and maintaining a healthy metabolism.
- Rich in Fiber for Digestion
Dietary fiber in quinoa promotes better digestion, prevents constipation, and supports gut health. A fiber-rich diet can also lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Low Glycemic Index for Blood Sugar Control
Quinoa has a glycemic index of around 53, which is considered low. This means it releases sugar slowly into the bloodstream, making it ideal for individuals with diabetes or those aiming to maintain stable energy levels.
- Supports Heart Health
Quinoa’s high magnesium and potassium content help regulate blood pressure. Additionally, its unsaturated fats and antioxidants may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Gluten-Free Alternative
For people with gluten intolerance or celiac disease, quinoa is a great alternative to wheat-based grains like barley or rye. It’s naturally gluten-free yet provides similar versatility in recipes.
- Rich in Antioxidants
Quinoa is packed with antioxidants that fight free radicals in the body, reducing inflammation and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s.
- Beneficial for Bone Health
With minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, and calcium, quinoa supports strong bones and may prevent osteoporosis, especially in older adults.
Potential Drawbacks of Quinoa
While quinoa is undoubtedly nutritious, it’s not without its downsides. Here are a few considerations:
- Saponins: The Bitter Coating
Quinoa seeds are coated with saponins, natural compounds that can taste bitter and may cause digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals. Washing or rinsing quinoa thoroughly before cooking removes most of these saponins.
- Caloric Density
Although nutrient-dense, quinoa is relatively high in calories compared to vegetables or plain grains. Overconsumption without portion control could lead to unintended weight gain.
- May Cause Allergic Reactions
In rare cases, quinoa may cause allergies. Symptoms might include itching, swelling, or digestive issues. If you suspect an allergy, consult a doctor.
- High in Oxalates
Quinoa contains oxalates, which may contribute to kidney stone formation in susceptible individuals. If you’re prone to kidney stones, moderate your intake.
Who Should Eat Quinoa?
- Vegetarians and Vegans
Quinoa is a lifesaver for those avoiding animal-based proteins, thanks to its complete amino acid profile.
- People with Gluten Intolerance
As a naturally gluten-free food, quinoa is ideal for those with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
- Athletes and Active Individuals
With its combination of protein and carbohydrates, quinoa is an excellent pre- or post-workout meal for energy and recovery.
- Diabetics and Heart Patients
Due to its low glycemic index and heart-friendly nutrients, quinoa can be a regular part of a diabetes- or heart-healthy diet.
How to Incorporate Quinoa into Your Diet
Quinoa is incredibly versatile and can be used in various recipes. Here are a few ideas:
- Breakfast Bowls
Cook quinoa with almond milk, cinnamon, and honey for a nutritious start to your day. Top with fresh fruits and nuts.
- Salads
Combine cooked quinoa with vegetables, herbs, and a light vinaigrette for a refreshing and filling salad.
- Quinoa Stir-Fry
Use quinoa as a base instead of rice for stir-fried dishes. Add tofu, chicken, or shrimp for protein.
- Soups and Stews
Add quinoa to soups and stews for added thickness and nutrition.
- Quinoa Flour
Quinoa flour can be used for baking bread, pancakes, or cookies as a gluten-free alternative.
How to Cook Quinoa
Cooking quinoa is simple:
- Rinse 1 cup of quinoa thoroughly under cold water to remove saponins.
- Combine the quinoa with 2 cups of water or broth in a pot.
- Bring to a boil, then reduce to a simmer and cover.
- Cook for 15 minutes or until the quinoa has absorbed all the liquid.
- Fluff with a fork and serve.
Quinoa vs. Other Grains
Here’s how quinoa compares to popular grains like rice and wheat:
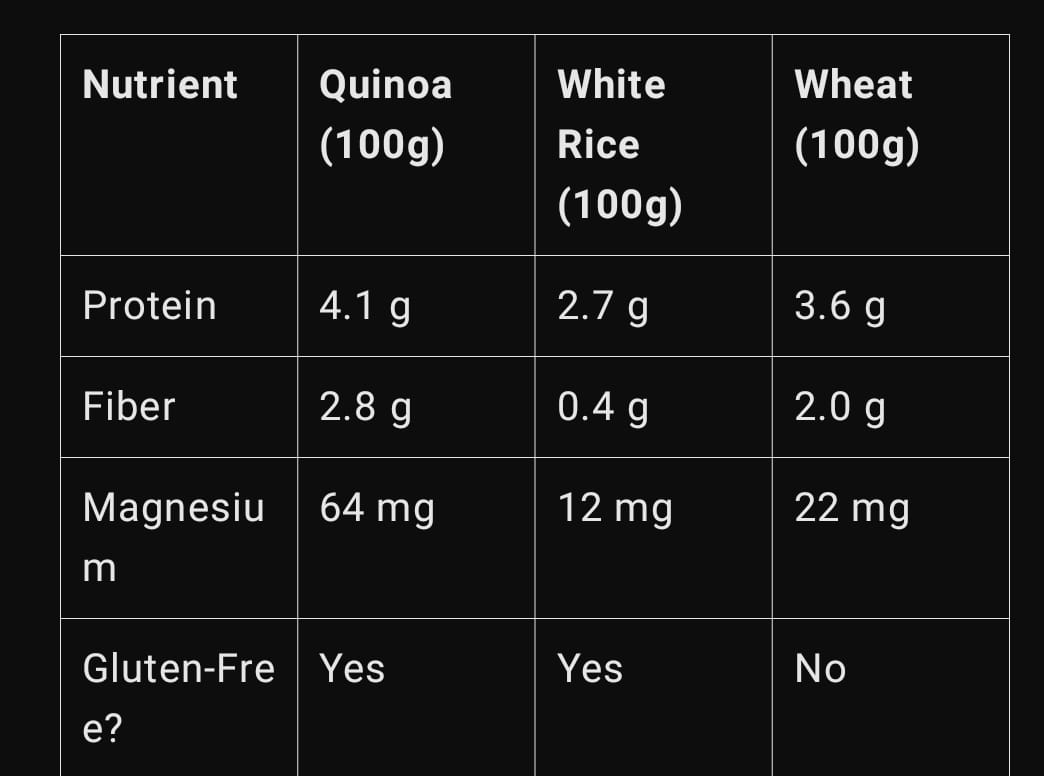
Final Verdict: Is Quinoa Good for Health?
Yes, quinoa is undoubtedly a healthy addition to most diets. Its high protein content, rich nutrient profile, and versatility make it a valuable food for people of all ages. However, it’s essential to consume it in moderation and balance it with other nutritious foods.
If you’re looking to diversify your meals, boost your protein intake, or explore gluten-free options, quinoa is a fantastic choice. Just remember to rinse it well before cooking, and experiment with various recipes to keep your meals exciting and flavorful.
Quinoa is more than just a trend—it’s a nutrient-packed superfood that deserves its place in your kitchen.



