Health Desk
Sandeep Dhand Ludhiana
Nutritionist And Health Educator
Introduction
Cancer is one of the most serious health challenges faced by people all over the world. It occurs when abnormal cells in the body grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts. Although many cancers exist, breast cancer, lung cancer, and prostate cancer are among the most common types found in adults. Early detection, proper treatment, and lifestyle changes—especially nutrition—play a major role in managing cancer and improving quality of life.
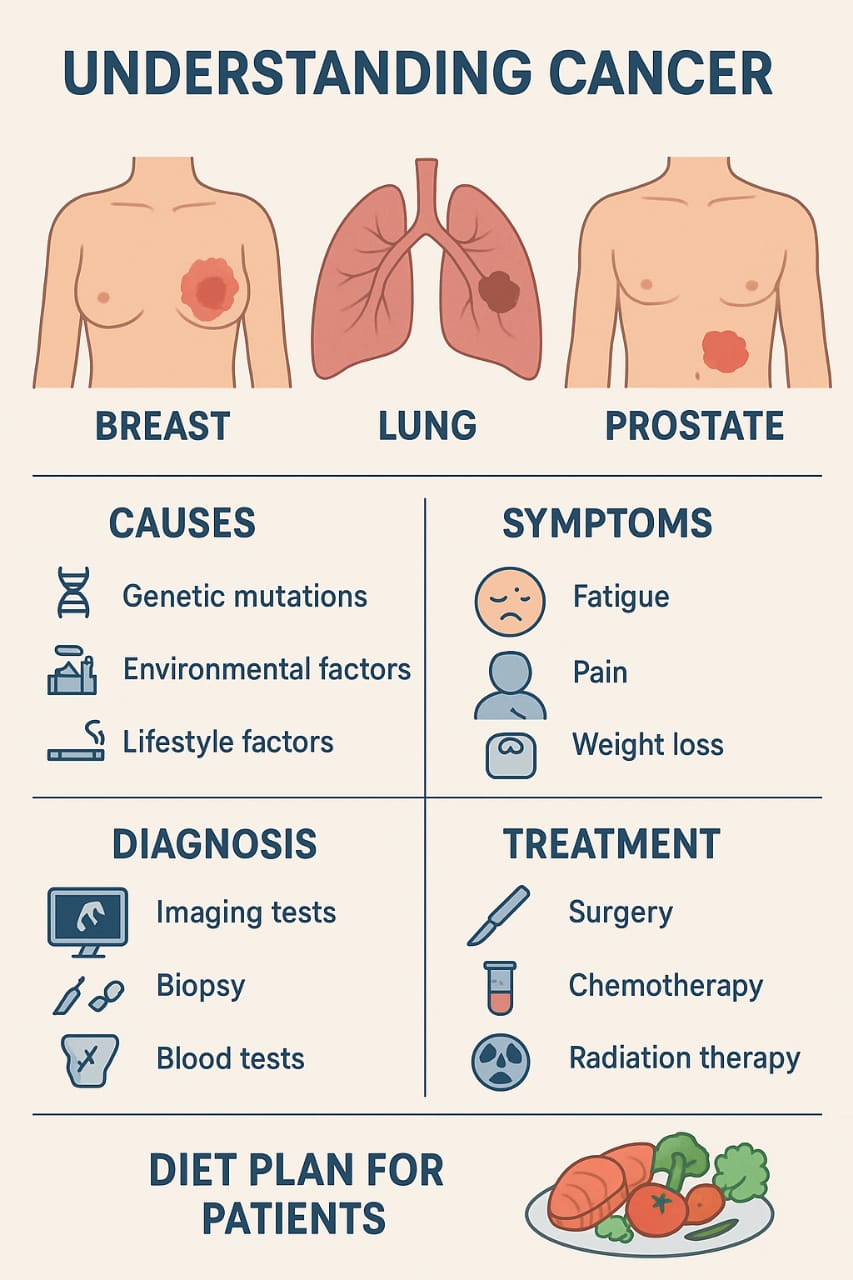
This article explains cancer in simple language, covering how it develops, the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and a complete diet plan for cancer patients. Whether you are a patient, caregiver, student, or health educator, this article will help you understand cancer deeply and practically.
WHAT IS CANCER?
Cancer begins in the body’s cells. Normally, cells grow, divide, and die in a controlled manner. But when genetic damage occurs, cells start multiplying rapidly without control. These abnormal cells form a mass called a tumor.
Types of Tumors
A. Benign tumor
Non-cancerous
Does not spread
Usually slow growing
B. Malignant tumor
Cancerous
Grows aggressively
Can spread to other parts of the body through blood or lymph
This spreading process is called metastasis
RISK FACTORS FOR CANCER
Cancer develops due to a combination of factors. Not all causes are in our control, but many are preventable.
A. Genetic Factors
Family history
Inherited mutations (BRCA1, BRCA2 in breast cancer)
B. Lifestyle Factors
Smoking
Alcohol
Unhealthy diet
Physical inactivity
Obesity
C. Environmental Factors
Radiation exposure
Polluted air (linked strongly to lung cancer)
Chemicals and industrial toxins
D. Hormonal Factors
High estrogen exposure in women
Testosterone imbalance in men (linked with prostate issues)
E. Age
Cancer risk increases with age
Most breast and prostate cancer cases occur after 50
BREAST CANCER
What is Breast Cancer?
Breast cancer occurs when abnormal cells begin growing in breast tissue. It affects both women and men, but women are at a much higher risk.
Causes
Genetic mutations (BRCA1 & BRCA2 genes)
Hormonal imbalance
Long-term hormone replacement therapy
Late pregnancy or not breastfeeding
Obesity
Alcohol consumption
Common Symptoms
Lump in the breast
Change in breast shape or size
Nipple discharge (sometimes bloody)
Skin dimpling (orange-peel texture)
Pain in breast or armpit
Diagnosis
Mammography
Breast ultrasound
MRI
Biopsy (definitive diagnosis)
Treatment
Treatment depends on stage and type.
A. Surgery
Lumpectomy (tumor removal only)
Mastectomy (entire breast removal)
B. Chemotherapy
Uses strong medicines to kill cancer cells.
C. Radiation Therapy
High-energy rays destroy cancerous tissue.
D. Hormone Therapy
Reduces estrogen effects (Tamoxifen, Aromatase inhibitors).
E. Targeted Therapy
E.g., Trastuzumab (Herceptin) for HER2-positive cancer.
LUNG CANCER
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer begins in the cells of the lungs. It is one of the leading causes of cancer deaths worldwide.
Causes
Smoking (main cause in 85% of cases)
Secondhand smoke
Air pollution
Radon exposure
Family history
Asbestos exposure
Symptoms
Persistent cough
Coughing blood
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Unintentional weight loss
Frequent lung infections
Diagnosis
Chest X-ray
CT scan
PET scan
Bronchoscopy
Biopsy
Treatment
Depends on type: Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or Small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
A. Surgery
If cancer is detected early.
B. Radiation Therapy
C. Chemotherapy
D. Immunotherapy
Helps immune system attack cancer.
E. Targeted Therapy
EGFR, ALK inhibitors used for specific gene mutations.
PROSTATE CANCER
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer occurs in the prostate gland of men. It is common after age 50.
Causes
Age
Family history
High-fat diet
Obesity
Hormonal factors
Genetic mutations
Symptoms
Early prostate cancer often has no symptoms. Advanced stages may show:
Difficulty urinating
Weak urine flow
Blood in urine or semen
Pain in hips or lower back
Erectile dysfunction
Diagnosis
PSA test (Prostate-Specific Antigen)
Digital rectal exam (DRE)
Biopsy
MRI/CT scan
Treatment
Depends on stage.
A. Active Surveillance
For slow-growing cancer.
B. Surgery (Prostatectomy)
C. Radiation Therapy
D. Hormone Therapy
Reduces testosterone.
E. Chemotherapy
F. Immunotherapy
COMMON SIDE EFFECTS OF CANCER TREATMENT
Cancer treatment affects both cancer cells and healthy cells.
Common Side Effects
Nausea & vomiting
Loss of appetite
Weight loss
Weakness
Mouth sores
Hair loss
Constipation or diarrhea
Low immunity
Taste changes
Proper nutrition plays a major role in recovery and strengthening the immune system.
NUTRITION AND DIET FOR CANCER PATIENTS
Nutrition is one of the most important parts of cancer care. A good diet helps:
Improve strength
Maintain body weight
Reduce side effects of treatment
Support immunity
Promote healing
Below is a complete, easy-to-follow cancer diet plan.
BEST FOODS FOR CANCER PATIENTS
A. High-Protein Foods
Cancer patients often lose muscle mass. Protein supports repair and immunity.
Paneer
Curd
Milk
Eggs
Dal, chana, rajma
Soya
Chicken or fish (if non-veg)
Peanut butter
Nuts and seeds
B. Healthy Carbohydrates
Provide energy.
Oats
Dalia
Brown rice
Whole wheat chapati
Sweet potato
C. Healthy Fats
Help reduce inflammation.
Olive oil
Coconut
Flaxseed
Walnuts
Chia seeds
D. Antioxidant-Rich Foods
Help fight free radicals.
Blueberries
Strawberries
Apples
Pomegranate
Turmeric
Green tea
E. Vegetables
Especially cruciferous vegetables:
Broccoli
Cauliflower
Cabbage
Spinach
Carrots
Beetroot
F. Hydration
Very important, especially during chemo.
Water
Coconut water
Herbal teas
ORS
Vegetable soups
FOODS TO AVOID FOR CANCER PATIENTS
Avoid:
Junk food
Processed meat
Deep fried foods
Excess salt
Too much sugar
Alcohol
Cigarettes or tobacco
Soft drinks
Packaged juices
Foods with preservatives
1-DAY SAMPLE DIET PLAN FOR CANCER PATIENTS
Morning (Empty Stomach)
Warm water + turmeric
OR
Aloe vera juice + 1 tsp honey
Breakfast
Oats porridge + fruits
OR vegetable upma
OR boiled eggs
OR paneer paratha with curd
Mid-Morning Snack
Coconut water
OR apple/papaya
OR handful of nuts
Lunch
2 chapati (multigrain)
Dal or paneer
1 cup vegetables
Brown rice (small portion)
Beetroot salad
Evening Snack
Green tea
Roasted chana
OR vegetable soup
Dinner
Vegetable khichdi
OR dal + rice (soft)
OR grilled chicken/fish (non-veg patients)
Light sabzi
Before Bed
Turmeric milk
OR chamomile tea
DIET PLAN FOR BREAST CANCER PATIENTS
Recommended
Soy products (tofu, soya milk)
Omega-3 rich foods
Berries
Spinach
Whole grains
Avoid
High-fat foods
Processed meat
Excessive sweet foods
DIET PLAN FOR LUNG CANCER PATIENTS
Recommended
Antioxidant-rich fruits
Citrus fruits (Vitamin C)
Garlic
Ginger
Green leafy vegetables
Protein-rich foods
Avoid
Alcohol
Deep-fried foods
Red meat in excess
DIET PLAN FOR PROSTATE CANCER PATIENTS
Recommended
Tomatoes (lycopene)
Pumpkin seeds
Broccoli
Green tea
Whole grains
Nuts
Avoid
High dairy intake
Processed foods
Red meat in excess
LIFESTYLE TIPS FOR CANCER PATIENTS
Eat small, frequent meals
Stay hydrated
Light walking daily
Avoid stress
Practice yoga/meditation
Take enough sleep
Avoid smoking and alcohol
Follow doctor’s medication and treatment schedule
CONCLUSION
Cancer—whether breast, lung, or prostate—is a serious but manageable disease when detected early and treated properly. Medical treatment combined with good nutrition, emotional support, and lifestyle changes can dramatically improve recovery and quality of life. Diet plays a major role in boosting immunity, reducing treatment side effects, and helping the body stay strong.
A balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, proteins, healthy fats, and whole grains is essential for every cancer patient. With holistic care and awareness, cancer management becomes easier and more effective.