Economic Desk
Tv10 Punjab
2 February
Journalist Sandeep Dhand Ludhiana
The presentation of the Union Budget 2026-27 by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman marks a historic milestone in India’s fiscal journey. Delivering her ninth consecutive budget under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, the Finance Minister outlined a vision that balances immediate relief for the common man with long-term structural reforms. Set against a backdrop of global trade tensions and shifting geopolitical dynamics, the budget emphasizes fiscal discipline, infrastructure expansion, and a digital-first approach to governance.

- Fiscal Discipline and Economic Health
At the heart of the 2026-27 budget is a commitment to maintaining a healthy balance sheet for the nation. The Finance Minister announced a total budget size of ₹53.5 lakh crore, with a clear focus on reducing the fiscal deficit.
Fiscal Deficit: The deficit is projected to fall to 4.3% of GDP for FY27, down from 4.4% in FY26.
Debt-to-GDP Ratio: The government aims to bring this ratio down to 55.6% from the current 56.1%.
Market Borrowing: Gross market borrowing is estimated at ₹17.2 lakh crore, while net tax receipts are projected at ₹28.7 lakh crore.
- Tax Reforms and the New Income Tax Act
A major highlight of this session was the announcement of the Income Tax Act, 2025, which is set to come into effect on April 1, 2026. This act aims to simplify the tax code and provide a more rule-based, automated experience for taxpayers.
No Change in Slab Rates: To the relief of many, personal income tax rates remain unchanged.
Revised Returns: The deadline for filing revised returns has been extended from December 31 to March 31 (with a nominal fee).
ITR Filing Extension: For non-audit businesses, the ITR filing date has been moved to August 31.
Capital Gains on Buybacks: In a significant shift, earnings from share buybacks will now be taxed as capital gains for all categories of shareholders.
- Boosting Infrastructure and Connectivity
The government continues its “Capex” (Capital Expenditure) heavy strategy to fuel growth. The allocation for government capital expenditure has been increased to ₹12.2 lakh crore.
Railways: The budget proposes seven new high-speed corridors and a massive Dedicated Freight Corridor connecting Dankuni (West Bengal) to Surat (Gujarat).
Urban Development: Cities with populations exceeding 500,000 will receive specialized focus for infrastructure upgrades.
Shipping & Waterways: New initiatives include an incentive package for manufacturing Sea Planes and the establishment of a ship-repair ecosystem in Varanasi and Patna.
- Sector-Specific Relief: What Gets Cheaper and Dearer?
The budget direct impacts the daily life of citizens through adjustments in customs duties and taxes.
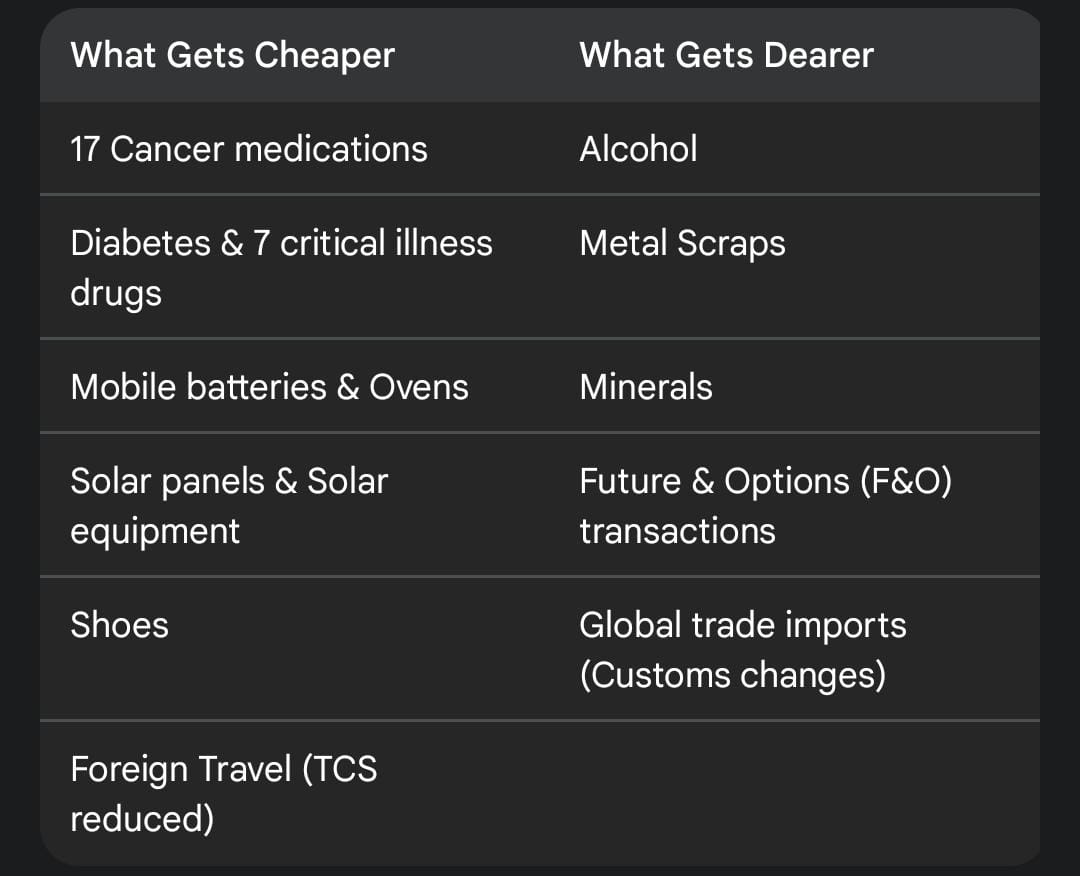
TCS Reductions: In a major move for the middle class, the Tax Collected at Source (TCS) on foreign tour packages and LRS (for education and medical purposes) has been slashed from 5% to 2%.
- Innovation, Technology, and the Digital Future
India is positioning itself as a global hub for data and technology.
Data Centers: Foreign companies providing global services via Indian data centers will enjoy a tax holiday until 2047.
Electronic Manufacturing: The budget for this sector has been hiked to ₹40,000 crore.
SME Growth Fund: A ₹10,000 crore fund has been proposed to create “future champions” among small and medium enterprises.
Space & Science: Funds have been allocated to upgrade telescope infrastructure and promote mountaineering.
- Social Welfare and Agriculture.
The “Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas” philosophy remains central to the budget’s social agenda.
Education: Every district in India will now have a government hostel for girls.
Health: The budget proposes the establishment of NIMHANS-2 and three new All India Institutes of Ayurveda.
Agriculture: Focus is shifting to high-value crops like coconut, sandalwood, and walnuts. A “Coconut Promotion Scheme” was specifically mentioned to boost productivity.
Animal Husbandry: A capital subsidy scheme for veterinary colleges and diagnostic labs was introduced to strengthen the rural economy.
The Political and Market Reaction
The budget received mixed reviews. While the government hailed it as a “Reform Express” on track with over 350 reforms implemented, the Opposition (Congress) described it as “pale” and “lacking transparency.”
The stock market reacted with volatility. While the Sensex and Nifty opened with gains, the hike in Security Transaction Tax (STT) on Futures & Options (raised to 0.05% and 0.15% respectively) led to a cooling off in trading sentiment. Metal stocks, particularly Vedanta and Hindustan Zinc, saw sharp declines following a drop in global gold and silver prices.
Conclusion: A Vision for 2047
Budget 2026-27 is clearly designed with the “Viksit Bharat 2047” (Developed India) goal in mind. By combining fiscal prudence with targeted incentives for emerging industries like Bio-Pharma and Cloud Computing, the government is attempting to insulate the Indian economy from global shocks while ensuring that the benefits of growth reach the marginalized.